Nowadays technology advances to happen very rapidly in all areas of life. So also in medicine, advances in technology have been used for examination and treatment of a disease. As an example which will be discussed here is the use of LASIK to correct eye defects such as: miopi (nearsightedness), hipermetropi (farsightedness) and Astigmatism (cylinder).
 Previously, before the invention of Lasik Mata technology, the means used to correct eye defects is with conventional surgery. This action has a very big risk because it can cause blindness. However, with the invention of LASIK technology community concerns began to fade. Then the question is whether the LASIK technology is completely safe for the eyes?
Previously, before the invention of Lasik Mata technology, the means used to correct eye defects is with conventional surgery. This action has a very big risk because it can cause blindness. However, with the invention of LASIK technology community concerns began to fade. Then the question is whether the LASIK technology is completely safe for the eyes?
LASIK (Laser Assisted In-situ keratomileusis) is an action with laser refractive eye surgery conducted by oftalmologis to improve miopi, hipermetropi, and Astigmatism.
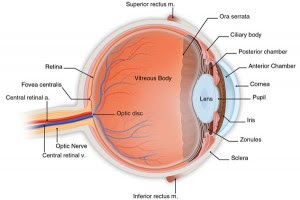
Before we continue the discussion about LASIK, it helps us discuss a bit about the anatomy of the eye, especially the role in action this LASIK.
Human eyeball has three layers:
1. Fibrous layer (outer coat), consisting of sclera and cornea
Sclera composed of fibrous layer wrapped 5 / 6 the back of the eyeball. Section front for vision through the conjunctiva bulbaris ("the white of the eye").
The cornea is the transparent part of the fibrous coat that wraps 1 / 6 the front of the eyeball.
2. Vascular layer (middle coat), consisting of the choroid, the body cilia, and sliced
Choroid, a layer of dark reddish-brown between the sclera and retina, forming the bulk of the vascular layer of the eyeball.
Connecting cilium Agency choroid with iris.
Iris is a section near the front surface of the lens.
3. Layer in (a coat in), consisting of the retina that has the optic and non-visual section
Optic section to visualize the light sensitive retina and has two layers: a layer of neutral and pigment cell layer.
Retinal non-visual part is the continuation of the pigment cell layer and the layer of cells that pass through the rear surface of the cilia of the retina and iris.
How is LASIK procedure?
Some procedures performed LASIK in action:
1. Preoperative
The use of contact lens is usually stopped approximately 5-21 days before surgery. Before surgery, the cornea of patients examined using pakimeter to measure its thickness and with a topografer to measure surface contours. By using low-power lasers, a topografer create a corneal topography map. This process is performed to detect Astigmatism and corneal deformities other. Using this information, the surgeon calculates the amount and location of corneal tissue to be removed when operating. Usually the patients were prescribed antibiotics prior to this action to reduce the risk of infection after the procedure is executed.
2. Operative
Performed when patients get up and move. Sometimes the patient is given a mild sedative, like Valium and anesthetic eye drops. Three action steps LASIK:
* Flap Creation
A corneal suction ring applied to the eye, make eyes in place (so do not moving). This step can sometimes cause bleeding (subconjunctival hemorrhage) in the sclera. These are mild side effects that can be experienced for several weeks. Increased suction caused blurred vision for a while. This process
* Done with a mechanical mikrokeratomi using metal blade or a femtosecond laser microkeratome (intraLASIK). A hinge (hinge) left at the end of this flap. Flap later reversed, reveal the stroma, the middle of the cornea. The process of removal and reversal may be less comfortable.
* Laser Remodeling
The second step uses eximer laser (193 nm) to change the shape of the cornea stroma. Laser vaporizes tissue without damaging the stroma. To erode the network does not need fire or cutting. Layer of tissue is taken ten micrometers in thickness. The use of laser ablation in the deeper corneal stroma causes acceleration of improvement of visualization and generate less pain than the earlier technique, photorefractive keratectomy (PRK).
Patient's perspective will be very unclear when the flap is lifted. Patients can only see a white light surrounding the orange laser light.
* Reposition of Flap
After laser re-established stromal layer, the flap returned to its position carefully by the surgeon, and checked the air bubbles, debris with appropriate action on the eye.
3. Postoperative
Patients are usually given antibiotic eye drops and anti-inflammatory for a few weeks after surgery. Patients are also told to sleep more and wear sunglasses to protect eyes from light, avoid so as not to rub eyes when not sleeping, and reduce eye dryness. Patients should follow the surgeon's recommendation to reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
What are the complications of this surgery?
Subconjunctival hemorrhage (the whites of the eyes appear red because of bleeding) is a common minor complication after LASIK action. While the most common complications of refractive surgery is the incidence of dry eye.
The risk for patients experiencing visual disturbance side effects, such as: hello, double visualization (ghosting), loss of contrast sensitivity (Foggy vision) and glare after LASIK depends on the degree of ametropia before surgery and other risk factors. Therefore, it is important to calculate the potential risk of a patient and not just the average estimate of likelihood for all patients.
Similarly, a brief description of LASIK. Viewed from the benefits and complications caused, while this LASIK surgery is more profitable than conventional surgery. However, because the action is still very new LASIK could have been the possibility of this action is more dangerous than the previous action.
 Previously, before the invention of Lasik Mata technology, the means used to correct eye defects is with conventional surgery. This action has a very big risk because it can cause blindness. However, with the invention of LASIK technology community concerns began to fade. Then the question is whether the LASIK technology is completely safe for the eyes?
Previously, before the invention of Lasik Mata technology, the means used to correct eye defects is with conventional surgery. This action has a very big risk because it can cause blindness. However, with the invention of LASIK technology community concerns began to fade. Then the question is whether the LASIK technology is completely safe for the eyes?LASIK (Laser Assisted In-situ keratomileusis) is an action with laser refractive eye surgery conducted by oftalmologis to improve miopi, hipermetropi, and Astigmatism.
Before we continue the discussion about LASIK, it helps us discuss a bit about the anatomy of the eye, especially the role in action this LASIK.
Human eyeball has three layers:
1. Fibrous layer (outer coat), consisting of sclera and cornea
Sclera composed of fibrous layer wrapped 5 / 6 the back of the eyeball. Section front for vision through the conjunctiva bulbaris ("the white of the eye").
The cornea is the transparent part of the fibrous coat that wraps 1 / 6 the front of the eyeball.
2. Vascular layer (middle coat), consisting of the choroid, the body cilia, and sliced
Choroid, a layer of dark reddish-brown between the sclera and retina, forming the bulk of the vascular layer of the eyeball.
Connecting cilium Agency choroid with iris.
Iris is a section near the front surface of the lens.
3. Layer in (a coat in), consisting of the retina that has the optic and non-visual section
Optic section to visualize the light sensitive retina and has two layers: a layer of neutral and pigment cell layer.
Retinal non-visual part is the continuation of the pigment cell layer and the layer of cells that pass through the rear surface of the cilia of the retina and iris.
How is LASIK procedure?
Some procedures performed LASIK in action:
1. Preoperative
The use of contact lens is usually stopped approximately 5-21 days before surgery. Before surgery, the cornea of patients examined using pakimeter to measure its thickness and with a topografer to measure surface contours. By using low-power lasers, a topografer create a corneal topography map. This process is performed to detect Astigmatism and corneal deformities other. Using this information, the surgeon calculates the amount and location of corneal tissue to be removed when operating. Usually the patients were prescribed antibiotics prior to this action to reduce the risk of infection after the procedure is executed.
2. Operative
Performed when patients get up and move. Sometimes the patient is given a mild sedative, like Valium and anesthetic eye drops. Three action steps LASIK:
* Flap Creation
A corneal suction ring applied to the eye, make eyes in place (so do not moving). This step can sometimes cause bleeding (subconjunctival hemorrhage) in the sclera. These are mild side effects that can be experienced for several weeks. Increased suction caused blurred vision for a while. This process
* Done with a mechanical mikrokeratomi using metal blade or a femtosecond laser microkeratome (intraLASIK). A hinge (hinge) left at the end of this flap. Flap later reversed, reveal the stroma, the middle of the cornea. The process of removal and reversal may be less comfortable.
* Laser Remodeling
The second step uses eximer laser (193 nm) to change the shape of the cornea stroma. Laser vaporizes tissue without damaging the stroma. To erode the network does not need fire or cutting. Layer of tissue is taken ten micrometers in thickness. The use of laser ablation in the deeper corneal stroma causes acceleration of improvement of visualization and generate less pain than the earlier technique, photorefractive keratectomy (PRK).
Patient's perspective will be very unclear when the flap is lifted. Patients can only see a white light surrounding the orange laser light.
* Reposition of Flap
After laser re-established stromal layer, the flap returned to its position carefully by the surgeon, and checked the air bubbles, debris with appropriate action on the eye.
3. Postoperative
Patients are usually given antibiotic eye drops and anti-inflammatory for a few weeks after surgery. Patients are also told to sleep more and wear sunglasses to protect eyes from light, avoid so as not to rub eyes when not sleeping, and reduce eye dryness. Patients should follow the surgeon's recommendation to reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
What are the complications of this surgery?
Subconjunctival hemorrhage (the whites of the eyes appear red because of bleeding) is a common minor complication after LASIK action. While the most common complications of refractive surgery is the incidence of dry eye.
The risk for patients experiencing visual disturbance side effects, such as: hello, double visualization (ghosting), loss of contrast sensitivity (Foggy vision) and glare after LASIK depends on the degree of ametropia before surgery and other risk factors. Therefore, it is important to calculate the potential risk of a patient and not just the average estimate of likelihood for all patients.
Similarly, a brief description of LASIK. Viewed from the benefits and complications caused, while this LASIK surgery is more profitable than conventional surgery. However, because the action is still very new LASIK could have been the possibility of this action is more dangerous than the previous action.